Category Archives: League 2
League 2 analysis in different topics
What is the most effective tactic to score corner goal in League 2?
In the book “Soccer Tactics and Skills”, Charles Hughes (1987) argued that the best way to score corner goal consists of 3 factors:
- Near post
- Inswing
- Keep it simple (Variety on a theme, not variety on sole criteria of doing something different)
By analysing 178 League 2 corner goals, it would be tested whether his argument can be applied to League 2 or not.
There is not much difference in terms of the sides of corner. 50.6% of corners were from the left side of the goal.
Type of delivery
The above chart shows that most of the corner goals were delivered by inswing (61%). 30% of them were outswing and 9% of them were ground pass which included medium or short corner. The finding fits the argument of Hughes that inswing is the best way to score corner goal.
Delivery target area
In terms of delivery target area, the result is not as dominant as the result of delivery type. Although near post was the most popular delivery target area, it was not dominant with 36%. In fact, the percentages of mid-goal area and far post were close with 32% and 26%. 5% of corners were delivered to touchline area which means they were short corners. Only 1% of corners were medium corner which were delivered to the edge of the box for long shots. By looking at this chart, Hughes’s argument about near post delivery is not very strong here because the difference between near post, mid-goal area and far post were within 10%. Near post is still a better choice but it is not a dominating factor as inswing delivery. Then the data would be compared with each other for in-depth analysis.
Which side vs. Type of delivery
The above chart shows that the preferences of delivery were different depending on which side of the corner it was. If the corner is taken at the left side of the goal, most of them were delivered by inswing. It could be explained by the fact that most of the players were right-footed. It is interesting to see which approach the team would use in the right side corner. 45 right side corner goals were delivered by inswing. That means teams chose a left-footed player to deliver the corner for the purpose of inswing delivery. However, 36 right side corner goals were delivered by outswing. This number is much more than the number of left side outswing corner (17). On the other hand, the numbers of ground pass delivery in both sides were similar. No matter which side we look at, inswing is still the most popular choice of delivery although it is more dominant in left side corner. In the right side corner, teams still prefer to do inswing delivery but there was considerable amount of outswing delivery also.
Type of delivery vs. Delivery target area
The above chart shows that inswing and near post combination scores the most corner goals (42). It fits the argument of Hughes. Another finding is that it is less likely to score corner goal at far post by outswing delivery (12 goals). The difference between inswing and outswing was less if the delivery target area is mid-goal area. The difference was 11 goals compared to the difference of near post (24 goals) and far post (23 goals). In short, for inswing delivery, it would be the best to deliver the ball to near post and far post, especially near post. For outswing delivery, it would be the best to deliver the ball to mid-goal area.
Keep it simple?
The result fits the argument of Hughes because 63% of corner goals were scored directly by the corner cross. 26% of corner goals were assisted by passing. Some teams may prefer to do flick-on headers to make assist but the data shows that it may not be a good choice because only 16% of corner goals were assisted by flick-on headers. If we consider passing assist only, flick-on header is a better choice than feet pass as shown in the chart with 6% more assists.
Conclusion
Reviewing the 3 factors mentioned by Hughes, I would say 2 of them were dominating factors in League 2: inswing delivery and keep it simple. They were proved by evidences. 61% of corner goals were delivered by inswing. 63% of corner goals were assisted by direct corner cross. However, the data shows that although near post is the best choice of delivery target area, it is not a dominating factor with 36% of corner goals delivered to near post. The same type of analysis could be applied to the data of different leagues and the results could be different.
Reference
HUGHES, C., 1987. Soccer Tactics and Skills. Great Britain: Queen Anne Press
Northampton – Stoke City in League 2? (Part 2)
In part 1, I have compared Northampton’s performance with other teams in League 2. It was clear that Northampton was strong in set play, particularly throw-in. Over 50% of their goals were from set play. In their set play goals, around 40% of them came from throw-ins. I will focus on analysing those 13 throw-in goals in this piece.
Time Analysis
No matter we consider the throw-in goals or all goals of Northampton; they both fit the general trend of time analysis in League 2 because more goals were scored in the later stage of the game. However, the key point is about the time slot of 76-90 minutes. 29.7% of goals were scored in this time slot in all goals. On the other hand, 38.5% of throw-in goals were scored in this time slot considering that the percentages in other time slots were only 15% at most. It shows that throw-in was an effective strategy for Northampton to use in the last 15 minutes of the game to score goals.
What were the assist styles?
Considering the assist styles, some teams may choose to do flick-on headers to make assist. In Northampton’s case, the best way to make assist is to make a direct throw-in passing by hands. 84% of the throw-in goals were assisted by hand passes, only 8% of them were assisted by flick-on header. It also means that at least 84% of the goals were scored by one-touch shot. The technical ability to make one-touch shot is one of the keys to score throw-in goals.
Goal Type
Many people may link throw-in goals to headers but it is not the case in Northampton. Even we found out that one-touch shot is important, the above chart shows that using feet to shoot is as important as header in scoring throw-in goals. Header goals were only 8% more than feet goals. If we consider the above two charts together, we realise that considerable amount of goals were scored by hand passing throw-in followed by shots made by feet. It may be a result not expected by some people.
Where were the assists made?
Since 84% of assists were from direct hand throws, only 7.7% of assists were from central area by flick-on header. It is worthy to note that 30.8% of assists were outside 18-yard from the goal line. Some teams may only use long throw tactics near penalty area but Northampton’s statistics show that it is worthy to do long throw outside the penalty area also.
Who scored the most throw-in goals?
Northampton did not rely on any particular player to score throw-in goals as the goals were widely distributed to 8 players. A Akinfenwa is the player who scored the most with 31% of throw-in goals considering he is a striker. The other 7 players scored 1 goal each. It is worthy to note that 15% (2 goals) were scored by own goals. It shows that one of the advantages in using long throw-in is to mess up the situation in penalty area so the defenders would have a higher chance to make a mistake scoring own goal.
Where they scored?
The above diagram obviously shows that the prime area for attacking long throws is the 12-yard area from the goal line. 84.6% of goals were scored in these two zones. Note that 15.4% of goals were scored outside the penalty area. My explanation is that most of the defenders would try to defend long throw-in by staying at the zones in front of the goal. It leaves space outside the penalty area for attackers to make long shot. It is worthy to note that no goal was scored in 12-18 yard area. It is because this zone is neither close enough for one-touch shot in long throws nor having enough space and time for players to make long shot.
Conclusion
By analysing Northampton’s strategy in throw-ins, we can identify why they are so strong in scoring throw-in goals. Firstly, they used a very direct style to attack. They didn’t prefer flick-on header as 84% of assists were came from direct hand throw-in passes. Secondly, one-touch shot is the key to score but we should be aware that using feet to score is almost as important as using header. Thirdly, Northampton did not rely on any particular player to be the target man to score throw-in goals. They had 8 players to score 11 throw-in goals (the other 2 goals were own goals). Fourthly, don’t ignore the importance of making delivery outside the penalty area (18-yard line) because 30% of their throw-in goals were delivered from zones outside the 18-yard line.
Northampton – Stoke City in League 2? (Part 1)
Stoke City is famous for their long throw-ins attacking strategy. It is a different kind of attack for the defenders who get used to crosses. It is also a big question for the keepers whether they should stay at the goal line or not. There are some pieces which analyse Stoke’s performance. Is there any other team having the same strategy in English football? Northampton may be the team with similar (or even better) performance in long throw-ins.
Top 5 teams in set play goals in League 2
Considering the number of set play goals, Northampton scored the most set play goals (34 goals). The following table shows the open play and set play goals of 24 League 2 teams this season and highlights the top 5 teams in set play goals. They are AFC Wimbledon, Bradford, Cheltenham, Gillingham and Northampton.
In order to analyse how important set play goals are to different teams, the percentage of set play goals were considered also. The following table shows the percentages of open play and set play goals of 24 League 2 teams this season.
For example, being the League 2 Champion, Gillingham scored 28 set play goals but there were stronger in scoring open play goals. Therefore, set play goals only accounted for 42.4% of their total goals. The top 5 teams with the highest percentage of set play goals were AFC Wimbledon, Aldershot, Bradford, Cheltenham and Northampton. Northampton is the 2nd place in set play goal percentage. 53.1% of their goals were set play goals. Comparing both tables to each other, we can identify that 4 teams existed in the top 5 positions in both tables. They are AFC Wimbledon, Bradford, Cheltenham and Northampton. That means these 4 teams were good at scoring set play goals and set play goals were more important to them. Note that Northampton and AFC Wimbledon are the only two teams scoring more set play goals than open play goals.
Throw-ins goals in League 2
This chart shows how strong Northampton was in throw-in goals. With most of the teams having 3 throw-in goals or less, Northampton scored 13 throw-in goals this season. They scored 100% more than the 4th place Bristol Rovers having 6 throw-in goals. The great difference shows that scoring throw-in goals was a strong weapon of Northampton while most of the teams didn’t have the ability to do so.
If we consider how important throw-in goals are within set play goals, Northampton is still the team showing the highest percentage. 38.24% of their set play goals were throw-in goals. It showed how important throw-in goals were to Northampton.
In fact, Gillingham and Northampton were the only 2 teams with more than 30% of their set play goals as throw-in goals. Considering only 9 teams in the league having more than 10% of their set play goals as throw-in goals, it shows how Northampton outperformed other teams by having 38.24%.
No matter we consider the number of throw-in goals or the percentage of throw-in goals, Northampton is still the best team in the league and they obviously outperformed other teams in the league.
I don’t have the goal scoring data of Stoke City this season. However, I wonder Stoke City can achieve the two conditions of Northampton or not.
- More than 50% of goals were set play goals
- Around 40% of set play goals were throw-in goals
In part 2, the focus will be analysing the details of Northampton’s throw-in goals. It includes when they scored, how they scored, where they scored, where the assists came from, etc.
League 2 2012/13 review: Top Scorer – Tom Pope
The top goal scorer in League 2 this season is Tom Pope, who is playing in Port Vale. He played every single game this season which means he had 46 league appearances. He scored 31 league goals. Port Vale had 87 league goals in total. Therefore, Pope has scored 35.6% of team goals. He is a tall striker with the height of 1.91m. He is 27 and will become 28 next season so he is at the peak of his career according to the analysis of optimum player age from Prozone.
How he scored?
In 31 goals, he scored 13 header goals, 9 goals by right foot and 9 goals by left foot. He is an all-round striker who can score goals through different ways. He is strongest at header goals (42%) and it is reasonable considering his height (1.91m). He is good at both feet as well because he scored considerable amount of goals through right and left foot.
Where he scored?
The above chart shows that Pope scored most of his goals in the 6-yard box (13 goals) and 6-12 yard area (13 goals). Considering 42% of his goals were header goals, it shows that he played like a target man inside the box and waited for the chances in the 12-yard area from the goal. Therefore, he is not good at long shot as he scored only 1 goal outside the penalty area.
When he scored?
The chart shows a characteristic of Pope. He was particularly strong at the 15-min period of both halves. He scored 8 goals in 16-30 mins and 61-75 mins periods. The phenomena was more obvious in the first half as he scored only 2 and 3 goals in the first 15 mins and last 15 mins in the first half.
Open play vs. Set play
The above two charts show the comparison of the Tom Pope and the team regarding the open play and set play goals. In Port Vale team, 74% of goals were open play goals. On the other hand, 81% of Pope’s goals were open play goals. That means Pope contributed for the team more in open play goals. He hadn’t scored any penalty this season. He had only 6 goals from set play.
Where the assists came from?
The above diagrams show that most of the assists were from the flanks (67.7%), especially the left flank (48.4%). 32.3% of assists were came from the middle zones. It shows that the delivery from the flanks were more suitable for Pope to score. It fitted the previous result showing that he is strong at header. This leads to an assumption that crossing should be the main source of the assist type which will be discussed in the following chart. The reason of 48.4% of assists in the left flank could be explained by Port Vale’s strength to attack through the left flank.
Types of Assist
The previous results show that Tom Pope is stronger at header and most of the assists were came from the flanks. The above chart supports the previous findings because it shows that crossing is the main source of the assist styles (45%). The “others” assist style included dribbling and regaining possession but these were not the main source of Pope’s goal. The second main assist style was passing (26%). It was related to the following analysis about the number of touch he used to score goals.
Number of Touch
68% of Pope’s goals were scored by one touch. It fitted the previous results showing that 45% of his goals were from crossing and 26 out of 31 goals were scored within the 12-yard area from the goal. His ability to score one-touch goals is a key to his playing style as a target man working mainly near the goal. Remember he is an all-round striker who is good at scoring goals by header, right foot and left foot. It helped him a lot to score one-touch goals.
Conclusion
To conclude, here are some key statistics and findings of Tom Pope’s 31 league goals this season (2012/13):
- He is an all-round striker with 42% header goals, 29% right foot goals and 29% left foot goals
- 26 out of 31 goals were scored with 12-yard area from the goal. It fits his playing style as a target man.
- He was particularly strong at the 15-min period of both halves (i.e. 16-30 mins and 61-75 mins). 16 out of 31 goals were scored in those 30-min periods.
- He was stronger at open play (81%) than set play (19%) comparing with the stats of the Port Vale team (74% vs. 26%).
- 67.7% of the assists were from the flanks, especially left flank (48.4%)
- Crossing was the main source of the assist style (45%)
- 68% of his goals were scored by one-touch
In order to bring out the best in Tom Pope, Port Vale should provide crosses from the flanks and let Pope stay at the 12-yard area from the goal for him to score one-touch goals in the coming season.
Header Goals Analysis in League 2 – Part 2
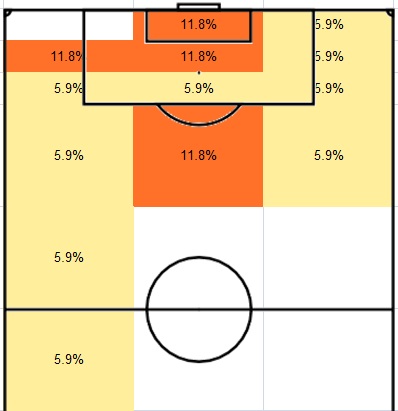
Continuing the header goals analysis from part 1, the set play header goals would be focused in this post. Note that all the goals data were updated to 3/1/2013 (same as part 1). The goal scoring patterns of header goals were different between open play and set play. The following diagram shows where the header goals were scored in set play.
Figure 1: Where set play header goals were scored
If we compare this diagram with the open play version in part 1, two main differences would be found. Firstly, the prime header goals scoring area of set play was the 6-yard box. This finding was different to the open play, where 6-12 yard was the prime header goals scoring area of open play. Secondly, in set play all the header goals were scored within 12 yards from the goal line. In open play, there were still 3.3% header goals scored outside the penalty spot. It shows that scoring header goals in open play and set play needs two different tactics. In open play, the difference of percentage of goals between 6-yard box and 6-12 yard was not too big, only 5.4% difference. However, in set play the difference became 31.4%. In other words, in set play the player should focus on delivering the ball into the 6-yard box. Otherwise, the chance of scoring header goals would be greatly reduced but it was not the case in open play.
Corner Header Goals
Many people may closely link corner goals to header goals because they assume header goals should be the dominating goal types of corner goals. However, statistics shows that it was the case in League 2.
This chart shows that header goals were the main source of corner goals but it was not a dominating factor. If the coach only focuses on scoring by header in corner set play training, he is ignoring the importance of scoring by feet. It was because 52 corner goals were scored by feet. For example, scoring by rebound or picking up the second ball. In this post, we will focus on how those 59 header corner goals were scored.
This chart shows that more corner goals were come from left side (44%) than right side (34%). The reason behind it was closely related to the types of delivery which would be discussed. This chart also shows that 78% (44%+34%) of corner header goals were directly assisted from corner delivery. The remaining 22% were come from short corner, header flick on or scoring in second phase of attack in corners. This finding shows the importance of getting the first touch in scoring corner header goals. The most effective way to score was the direct delivery.
In terms of delivery, inswinging cross was the best way of delivery. 41 corner header goals were scored by inswinging cross but only 17 corner header goals were scored by outswinging cross. Moreover, it was not a good idea to use any other delivery method (e.g. short pass or pass to the edge of the box) because only 1 goal was scored by other methods. Since most of the corner header goals were delivered by inswinging cross, it explained that more corner header goals were come from left side considering most players are right-footed.
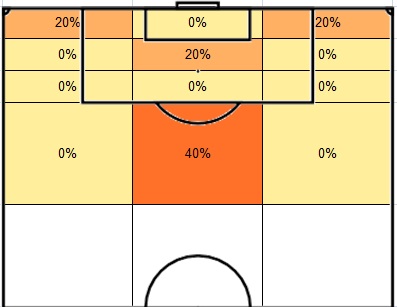
The area in front of the goal was divided into three different aim zones: near post, mid-goal area and far post. This chart shows that near post was the best place to be delivered to score corner header goals because 36% of goals were scored in near post. On the other hand, the percentages of mid-goal area and far post were similar (29% and 30%). The above two findings show that the inswinging corners delivered to the near post was the most effective way. It fits the argument of Hughes (1990) arguing that the theme that pays the highest dividend in corners is an inswinging corner to the near post in the book “The Winning Formula”.
Moreover, more than 90% of corner header goals were scored in the first phase. In other words, if the ball is cleared by defenders, the chance of scoring header goals would be greatly reduced even the ball is delivered into the penalty box again. By summing up the findings about corner goals, the best way of scoring corner header goals was to deliver inswinging corner from the left side to the near post and scored it in the first phase (first touch).
Free Kick Header Goals
Comparing with the corner goals, the header goals in free kick is less important which was shown in the following chart.
The most common goal type of free kick was to score by right foot. There were 32 header goals scored in free kick which was less than goals scored by right foot by 4.
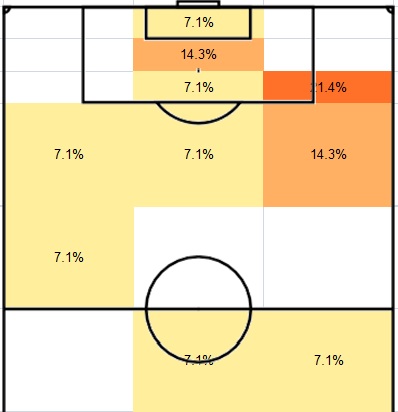
The best delivery zone of free kick header goals was found by considering where the assists came from.
Figure 2: Where free kick header goals were assisted
Firstly, the zones just outside the penalty box were the better areas for delivery because 62.5% of free kick header goals were delivered from these three zones. Secondly, right flank was better than left flank because 50% of free kick header goals were delivered from right flank. By combining both findings, it can be concluded that the best delivery zones for free kick header goals were the zones outside the penalty box in two flanks, especially the right flank (21.9% in left and 37.5% in right).
In terms of types of delivery, inswinging delivery was still the best way, which is the same finding from corner header goals. However, it should be noted that the difference between inswinging (18 goals) and outswinging (11 goals) was much smaller in free kick than in corner. In other words, higher percentage of header goals was scored by outswinging delivery in free kick than in corner.
Mid-goal area was the dominating factor in the delivery destination of free kick header goals. This finding was different from that in corner. In corner, near post was the best area to be delivered but mid-goal area was the best area in free kick. Moreover, the difference was greater in this chart as there was 29% difference between mid-goal area (59%) and far post (30%), while the difference was only 6% in corner. That mean the advantage of delivering to mid-goal area in free kick was more obvious than delivering to near post in corner.
By summing up the findings about free kick, the best way of scoring free kick header goals was making an inswinging delivery to the mid-goal area from the zone outside the penalty area in right flank.
Conclusion
Scoring header goals in set play need a different tactic than in open play as the prime goal scoring area was different. Even in the set play goals, header goals had different importance to different set plays. Header goals were the most important in corner but less important in free kick. Moreover, the most effective way of scoring header goals in corner and free kick were different. Therefore, coaches should separate the training of corner and free kick since the tactical needs were different.
Reference
HUGHES, C., 1990. The Winning Formula. London: Collins
Header Goals Analysis of League 2 – Part 1
How important are the header goals in League 2? Most of the goals are scored by right foot, left foot or head but they are not evenly distributed. Updated to 3/1/2013, there were 948 goals in League 2. 44% of them were scored by right foot, 25% by left foot, 21% by header and 10% of goals were scored by other parts of the body or by penalty. In short, around 1 out of 5 goals were scored by header. It fits the argument of Hughes (1990) saying that about 1 goal in every 5 overall was scored with a header in the book “The Winning Formula”.
On the other hand, I explained the importance of first goal before so let’s look at the impact of header goal in League 2 first goals. There were 317 first goals and 17% of them were scored by header. That means it was less likely to score first goal by header while the impact of right foot was increased to 50%. It shows that attacking in header may not be a good choice to score first goal in League 2.
If we focus on the 200 header goals which is shown in the following chart, 54% of header goals were came from set play while 46% of them came from open play.
The above chart shows that header goals were scored more in set play (54%) than in open play (46%). Corner is the main source of header goals in set play, having 29% of total header goals. The importance of header goals is more obvious if the data is normalised by considering the total number of open play and set play goals.
There were 619 open play goals in League 2. The number of open play goals was more than that of set play goals. Even 46% of header goals were from open play, it only took 15% of total open play goals. It shows that the impact of header goals was not obvious because 84% of open play goals were scored by feet, particularly more than half (55%) were scored by right foot. It shows that if a team want to score open play goals, they should focus working more on their feet rather than header.
On the other hand, there were 244 set play goals (exclude penalty) in League 2. 54% of header goals were came from set play and it took 44% of set play goals. It highlights the importance of header goals in set play comparing with the situation in open play goals shown in previous chart. It gives a clue for the teams which are stronger at header. They should focus more on attacking in set play because it will give 29% more chance to score by header. However, it is worthy to note that even header goals were more important in set plays; it still took less than half of set play goals. In other words, more than half of the set play goals were scored by feet. It is very important for the practice of set play in training as they may only focus on attacking by headers. However, statistics show that the goals scored by feet in set plays were more than that by headers.
In this post, only open play header goals would be analysed. The analysis of set play header goals would be discussed next week because there are 3 types of set play (corner, free kick and throw-in) to be analysed.
Open Play Header Goals
Crossing was the main source of open play header goals because 85% of them were assisted by cross.
The remaining 15% were assisted by passing or shots. It indicated that there is a close relationship between crossing and header goals.
Some people may argue that the prime goal scoring area of header goal in open play is the 6-yard box because it is closer to the goal. However, it is not the case in League 2.
Figure 1: Where open play header goals were scored
The above diagram shows that more than half (51.1%) of the open play header goals were scored in the 6-12 yard area while 45.7% of them were scored in 6-yard box. It is similar to the argument of Hughes (1990). He argued that the “prime target area” extends out 8 yards, from 2 yards inside the 6-yard box to the penalty spot, and across 20 yards, the width of the 6-yard box. In this analysis, it shows that the prime scoring area of header goals is the 12-yard area from the goal to the penalty spot. For any header shots made behind the penalty spot, the probability of scoring decreased dramatically because only 3.3% of open play header goals were scored behind the penalty spot.
Figure 2: where open play header goals were assisted
From previous finding, crossing was the main source of assist to open play header goals. Therefore, it is not surprised to see that most of the assists were come from both flanks. Horizontally, there is not much difference between the right and left side which took 41.3% and 45.7% of assists. On the other hand, there were differences by analysing vertically. The assists made from the 18-yard area from the goal (65.2%) were much more than that from the zones outside the penalty area (31.5%). It is worthy to note that if the ball is delivered outside the final third of the pitch, it is much less likely to score by header because only 3.3% of assists were came from outside the final third of the pitch. If the delivery is come from the right side, the best delivery would be crossing from wide or deep because they took 12% and 13% of assist. The pattern would be different in the left side. Crossing near the goal line was better.
Conclusion
By combining the 3 points mentioned above, the best formula to score open play header goals in League 2 was found. It should be assisted by crossing. The ball should be delivered into the 12-yard area from the goal. The delivery area should be the final 18-yard area from the goal at both flanks. On the other hand, header goals were more important in set play than in open play. However, the importance of header goals should not be over-emphasised because over half of the set play goals were scored by feet.
The set play header goals would be analysed next week.
Reference
HUGHES, C., 1990. The Winning Formula. London: Collins
Clean Sheets Analysis of League 2
A football game is all about attacking and defending. Therefore, keeping a clean sheet is as important as scoring goals. A team scoring a goal doesn’t guarantee any point but keeping a clean sheet guarantee at least one point and potentially getting three points. In this post, the defensive performance of League 2 teams would be discussed by analysing the clean sheets of League 2. Updated to January 28, there were 338 matches had been played, that means there were 676 team performances. Of these 676 team performances, 189 ended up with a clean sheet (28%). The teams produced 7.88 clean sheets on average. In these 7.88 clean sheets, 5.38 clean sheets led to wins and 2.50 clean sheets led to draws. On the other hand, clean sheets produced about 2.35 points per team and match on average.
The frequency of clean sheets is shown in the following chart.
As shown in the chart, there is a huge range in abilities to keep clean sheets (from 2 to 13). Fleetwood and Cheltenham performed much better than other team, producing 13 and 12 clean sheets. Part of their ability to generate points has been their ability to produce good defence. In the top 4 clean sheet producers (10 teams), only Accrington, Morecambe and Aldershot are in the bottom half of the table. It indicates two results. Firstly, good at keeping clean sheets can lead to good league positions. Secondly, it suggests that defence is not the main issue of the above 3 teams. In order to improve their league positions, they should focus on improving their attacking. Moreover, the bottom 2 clean sheet producers are Bristol Rover, Plymouth and Wimbledon. They are the bottom 3 teams in the League 2 table as well which indicates the importance of keeping clean sheet. On the other hand, it shows how strong Port Vale’s goal scoring was. Port Vale only produced 7 clean sheets which are below average. However, they are at the top of the table which means the high number of goal scored can overcome the weakness of their defence.
Clean sheets were of different value for different teams. This is shown in the following chart.
Clean sheets had enormous value (3 points) for Exeter and Wimbledon. For every single match they held clean sheet, they won the game and got 3 points. Note that Wimbledon is at the bottom of the league table. That means the biggest problem of Wimbledon right now is the defence, not attack. On the other hand, Plymouth had the worst performance in the above chart. It shows that even Plymouth had kept clean sheet, they only managed to 1.5 points on average. Considering both charts, it means that Plymouth is having problems in both attack and defence. In the top 5 teams in this chart, 4 of them are in the top 6 of the league table. In other words, it’s not only keeping clean sheets that’s important, but also how the team managed to get points from clean sheets.
By combining both charts together, the teams can be analysed from another perspective which is shown in the following diagram.
In this chart, the two axes are the two average numbers (2.35 points gained and 7.88 frequencies of clean sheets). The objective of using two average numbers as the axes is to divide 24 teams into four quadrants showing different abilities. Firstly, Bristol Rovers, Plymouth, Torquay and Rochdale are at the bottom left corner. The characteristic of the teams in this quadrant is that they are both weak at producing clean sheets and getting points from clean sheets. The opposite quadrant is the top right quadrant which means the teams were good at producing clean sheets and got points from clean sheets as well. Gillingham was the best performer in this quadrant which means Gillingham had a good balance of attack and defence. On the other hand, the top two performers of keeping clean sheets were in the bottom right quadrant, they should focus on improving their attacking because it was the main issue hindering both teams from getting points from clean sheets. The same argument could be applied to Aldershot and Morecambe as well since they are at the bottom half of the league table. Port Vale didn’t show why they can be the top of league table in this chart because they were weak in producing clean sheets. However, their efficiency is better than Gillingham by getting more points per clean sheet game.
To conclude, keeping clean sheets is a strong indicator of a team’s defending ability. However, it’s not only keeping clean sheets that’s important, but also how the team managed to get points from clean sheets. Therefore, by dividing 24 teams into four quadrants showing different characteristics, we can understand why some teams are doing better than others and which aspects (attacking or defending) should be the main focus point for team improvement.
Analysis of top 4 strikers in League 2 (2)
The analysis is continued following the first part last week (here). In the shot analysis, when treating unequal frequencies of starting appearances, the data are “normalised” by dividing the data by the frequency of starting appearances.
Although the other three strikers have at least 2.5 shots per appearance, T Pope had only 1.83 shots per appearance which is significantly lower than others. In terms of getting shot chances, T Pope is weaker than the other three strikers. On the other hand, A Akinfenwa showed his weakness as he only got 1.12 shots on target per appearance. N Wells and J Cureton are similar, both getting high number in shots and shots on target. Even T Pope got less chance to shoot; he still managed to get 1.48 shots on target which means he utilise the chances well. If you look at this chart only, you may wonder why T Pope is the leading goal scorer in League 2. It is all because he is particularly strong at catching the chances even the chances he get are less than others. This brings us to the next analysis chart: Accuracy rate vs Conversion rate.
Accuracy rate = no. of shots on target / no. of shots total
Conversion rate = no. of goals / no. of shots total
T Pope is outperforming others in this chart in both rates. In previous chart, N Wells and J Cureton showed they got more chances to shoot and they did well in number of shots on target. It is reflected in their decent accuracy rate (66% and 71%). However, conversion rate is their weakness (26%) and it explains why they can’t be the leading goal scorer even they got more chances. T Pope’s conversion rate (48%) is 22% more than them. A Akinfenwa did well in conversion rate (31%) but he is weak at accuracy rate (45%). From the above two charts, you may realise N Wells and J Cureton are so similar. They both good at getting shooting chance, have a decent accuracy rate but weak at converting chances into goals. T Pope is another type of striker who is highly efficient. A Akinfenwa strike a balance between both types.
In analysing where the strikers scored, we can find out other characteristics of the strikers. A Akinfenwa is weak at long shot because only 8% of his goals were scored outside 12 yards from the goal line. It is reasonable if we combine the finding last week suggesting that he is strong at scoring by headers and in set play. N Wells is strong at scoring in 6-yard box (67%). Last week, we found out that he hasn’t scored any goal by header. If we combine both together, I guess that his goal scoring style is like “poacher” to catch the chances in 6-yard box by using his agility rather than strength. T Pope and J Cureton had a good balance in goal scoring area with T Pope stronger at 6-yard box and J Cureton stronger at 12-18 yard area.
This chart fits our finding beforehand. A Akinfenwa is strong at heading and he scored 92% of his goals within 12-yard area from goal. It is reasonable to see that he scored all goals by using 2 touches or less. N Wells fits his “poacher” style by scoring all his goals using 2 touches or less. In terms of using 3 touches or more, T Pope had the highest percentage (20%). If we combine our finding of his high conversion and accuracy rate, it can somehow show his composure in front of the goal by getting the best chance to score.
We can find out the strikers’ particular goal scoring pattern by using time analysis. Firstly, A Akinfenwa is much stronger in second half, only 31% of his goals were scored in the first half. Note that 46% of his goals were scored in the last 30 minutes of the game. This may be explained by his strength and strong header to attack at the end of the game. N Wells haven’t scored any goal in the last 15 minutes of the game. It is reasonable if we sum up the previous findings. Usually there will be direct style and long ball in the last 10-15 minutes if a team is losing, but N Wells is not the same type of striker like A Akinfenwa. N Wells is strong at feet and agility rather than header and strength. T Pope’s goal scoring pattern is interesting. 70% of his goals were scored in the mid 15 minutes of the halves. Only 5% of goals were scored in the first 15 minutes of the halves. He may need time to “warm up” in the game before showing his goal scoring power. Then we move on to the assist analysis to see how the strikers’ goals were assisted.
J Cureton is stronger than others in dribbling which can create the scoring chance himself. A Akinfenwa and N Wells have no dribbling goals, that means they heavily rely on the support from teammates because they can’t create chances themselves. It is reasonable if we refer back to the characteristics of these two strikers. N Wells is strong at scoring in rebounds because 25% of his goals were assisted by teammates’ shots. It fits his “poacher” style mentioned above. Moreover, none of his goals were come from crossing. Surprisingly, only 20% of T Pope’s goals were assisted by passing. He relied on crossing (40%) more than other strikers. Then we analysed where the assists were. Please note that only open play goals assists were shown in the following diagrams.
A Akinfenwa:
As I mentioned last week, A Akinfenwa is strong at headers and set play. This diagram shows that his headers goals were heavily linked to set play. Therefore, only 40% of open play goals assists were from the flanks.
J Cureton:
J Cureton’s goals were mainly assisted from the right flank and centre. If any team play against Exeter, they should pay more attention to defending at their left flank (particularly from 12 yard to outside the penalty area) because 35.7% of J Cureton’s goals were assisted from these two zones.
N Wells:
This diagram further supports my previous arguments about the characteristics of N Wells. He is strong at agility and feet, weak at headers and strength. He plays like a “poacher” but none of his goals were come from crossing. Therefore, this diagram is under expectation that 83.3% of assists came from centre. By using this diagram, we know more about how he scored. 33.3% of assisted were from 12-18 yard area. If we combine this with the previous findings:
- 67% of his goals were scored in 6-yard box
- 50% of assists were passing, 25% of assists were shots
- 89% of goals were scored by feet
- 100% of goals were scored by 2 touches or less
We can figure out a full picture how he scored open play goals: his teammates attack through middle of the pitch, making a pass or take a shot (particularly 12-18 yard area). If it is a pass, he would at most take one touch before the shot. If it is a shot, he would take the rebounding chance in the 6-yard box.
T Pope:
From last week’s finding, T Pope is an all-round striker. He is good at scoring by right foot, left foot and header as well. Even in this assist diagram, the assists covered a wide range of areas. These make defending the leading goal scorer a difficult task. However, it is still a useful tip to find out that 41.3% of assists came from centre.
I think the whole analysis process covers enough details to find out the characteristics of the strikers. This is the end of the striker analysis. I may make a review about striker analysis at the end of the season.
Analysis of top 4 strikers in League 2 (1)
Different strikers have their own characteristics in scoring goals. They can somehow reflect their teams’ goal scoring characteristics as well. We will focus on the top 4 goal scorers in League 2. The analysis is quite long so I divide it into two posts. The second part will be continued next week. The following table shows who they are, their team and the position in league table. Please note that all the data is updated to 28/12/2012.
|
Name |
No. of goals |
Team |
Team league position |
|
T Pope |
20 |
Port Vale |
2nd |
|
J Cureton |
16 |
Exeter |
10th |
|
A Akinfenwa |
13 |
Northampton |
11th |
|
N Wells |
12 |
Bradford |
5th |
It seems that being a top team does not necessarily need a top goal scorer as only 2 of the top 4 strikers are playing for a team in the top 7 of the table which is the promotion playoff line. The other 2 strikers are playing for the teams in the mid-table position. However, I agree that a high quality striker can bring an average team into a top team.
Although T Pope is the top goal scorer, he doesn’t have the highest percentage of team goals. J Cureton is the striker whom the team relies on the most because he scored 47% of the team goals. It is worthy to note that all 4 strikers scored more than one-third of the team goals.
Apart from looking at the number of goals, we should analyse by looking at the starting appearance as well in order to understand the efficiency of the strikers.
As the top league goal scorer, T Pope is the most efficient striker as well. He scored 0.87 goals per starting appearance. Note that J Cureton scored more goals than A Akinfenwa but A Akinfenwa is more efficient because he scored slight more goals than J Cureton in terms of goals per starting appearance.
We discussed how important the first goal before (here) so it is worthy to analyse the strikers’ ability to scored the first goal in the match.
A Akinfenwa performed much better than other strikers in terms of first goal. 46% of his goals were first goal, which is obviously higher than that of T Pope (30%) and J Cureton (31%). His percentage of first goal is almost double the percentage of N Wells (25%). This is A Akinfenwa’s strength and people may ignore it if we don’t analyse the strikers from this perspective.
Then we move on to analyse the relationship between open play and set play goals.
T Pope (85%) and J Cureton (88%) scored most of their goals in open play, obviously higher than the percentage of other two strikers. N Wells struck a balance by scoring 50% open play goals. However, 25% of his goals were come from penalties. A Akinfenwa is particularly strong at scoring set play goals as 62% of his goals were from set play. Note than 31% of his goals were from throw-in which is much higher than other strikers. Moreover, he scored the highest percentage of goals in corner (15%) as well. He is a good example showing that the team top goal scorer can reflect the goal scoring characteristic of the team. Northampton scored more goals in set play (53%) than open play (47%). In all 18 set play goals, 50% of them were came from throw-in. The goal scoring pattern of Northampton and A Akinfenwa is almost the same even he scored only 35% of team goals.
Then we will analyse how the strikers scored the goals.
Note that I have excluded the goals from penalty in this chart. T Pope shows he is an all-round striker and this may explain why he is leading goal scoring table. The goals he scored by using his right foot (35%), left foot (30%) and head (35%) were almost evenly distributed. J Cureton is particularly strong at scoring goals by right foot (80%). However, it can be treated as a weakness as well because it is easier for the defender to mark him. N Wells is weak at header as he hasn’t scored any goal by header. However, he is strong at scoring goals by using both feet. A Akinfenwa is strong in air as he scored 58% of his goals by head. It fits what we find that he scored the highest percentage of goals from set play (62%) among 4 strikers, particularly in throw-in (31%) and corner (15%). In short, scoring goals by header in set play is the strongest weapon of A Akinfenwa.
The analysis will be continued next week by analysing these 4 strikers from different perspectives including where they scored, when they scored, where assist came from, assist types, shots total and shots on target.